Polygons and planes
The pin() function accepts an array of 3D points as well as singletons and pairs. In this case, the default graphical treatment is to apply the Luxor.poly(... :stroke) function to the array of projected 2D points.
Möbius
function makemobius()
x(u, v) = (1 + (v / 2 * cos(u / 2))) * cos(u)
y(u, v) = (1 + (v / 2 * cos(u / 2))) * sin(u)
z(u, v) = v / 2 * sin(u / 2)
w = 1
st = 2π / 150
Δ = 0.1
result = Array{Point3D,1}[]
for u in 0:st:2π-st
for v in -w:Δ:w
p1 = Point3D(
x(u, v + Δ / 2),
y(u, v + Δ / 2),
z(u, v + Δ / 2))
p2 = Point3D(
x(u + st, v + Δ / 2),
y(u + st, v + Δ / 2),
z(u + st, v + Δ / 2))
p3 = Point3D(
x(u + st, v - Δ / 2),
y(u + st, v - Δ / 2),
z(u + st, v - Δ / 2))
p4 = Point3D(
x(u, v - Δ / 2),
y(u, v - Δ / 2),
z(u, v - Δ / 2))
push!(result, [p1, p2, p3, p4])
end
end
return result # as an array of 3D polygons
end
# ... on a drawing
@drawsvg begin
background("grey20")
eyepoint(300, 300, 300)
perspective(1200)
setopacity(0.7)
sethue("white")
setline(0.4)
mb = makemobius()
for pgon in mb
pin(100pgon)
end
end 800 600This isn’t always going to be correct - although three 3D points always define a flat face in a 2D plane, more than three points don’t always do so.
The default action when pin() is called on a list of Point3Ds is poly(pts, fill), once the Point3Ds have been projected into 2D space as pts.
You can also pass a gfunction. It should accept two arguments: a list of Point3Ds and a list of Points. For example, this calls Luxor's poly() function on the list of 2D points in p2 that are the projections of the Point3Ds in pgon.
pin(pgon,
gfunction = (p3list, p2list) -> begin
poly(p2list, close=true, :fill)
end)In this example, the gfunction draws colored circles inside each square:
function makemobius()
x(u, v) = (1 + (v / 2 * cos(u / 2))) * cos(u)
y(u, v) = (1 + (v / 2 * cos(u / 2))) * sin(u)
z(u, v) = v / 2 * sin(u / 2)
w = 1
st = 2π / 160
Δ = 0.1
result = Array{Point3D,1}[]
for u in 0:st:2π-st
for v in -w:Δ:w
p1 = Point3D(
x(u, v + Δ / 2),
y(u, v + Δ / 2),
z(u, v + Δ / 2))
p2 = Point3D(
x(u + st, v + Δ / 2),
y(u + st, v + Δ / 2),
z(u + st, v + Δ / 2))
p3 = Point3D(
x(u + st, v - Δ / 2),
y(u + st, v - Δ / 2),
z(u + st, v - Δ / 2))
p4 = Point3D(
x(u, v - Δ / 2),
y(u, v - Δ / 2),
z(u, v - Δ / 2))
push!(result, [p1, p2, p3, p4])
end
end
return result # as an array of 3D polygons
end
# ... in a drawing
@drawsvg begin
background("grey20")
eyepoint(300, 300, 300)
perspective(1200)
mb = makemobius()
for (n, pgon) in enumerate(mb)
pin(100pgon,
gfunction = (p3list, p2list) -> begin
sethue(HSB(rand(200:300), 0.7, 0.8))
ellipseinquad(p2list, action=:fill)
end)
end
end 800 600Surfaces
A surface plot like the following also works quite well, mainly because each new polygon hides the ones behind it.
@draw begin
background("grey20")
perspective(500)
eyepoint(500, 500, 300)
k = 30
xmax = 4π
ymax = 4π
st = 0.3
f(x, y) = 2(sin(x) * cos(y)) + (cos(x) * sin(y))
sethue("blue")
setline(0.5)
for x in -xmax:st:xmax
for y in -ymax:st:ymax
sethue(HSB(360rescale(x, -xmax, xmax), 0.8, 0.8))
p1 = Point3D(k * x,
k * y,
k * f(x, y))
p2 = Point3D(k * x,
k * (y + st),
k * f(x, y + st))
p3 = Point3D(k * (x + st),
k * (y + st),
k * f(x + st, y + st))
p4 = Point3D(k * (x + st),
k * y,
k * f(x + st, y))
pin([p1, p2, p3, p4], gfunction=(p3s, p2s) -> begin
poly(p2s, close=true, :fill)
sethue("white")
poly(p2s, close=true, :stroke)
end)
end
end
axes3D(200)
end 800 600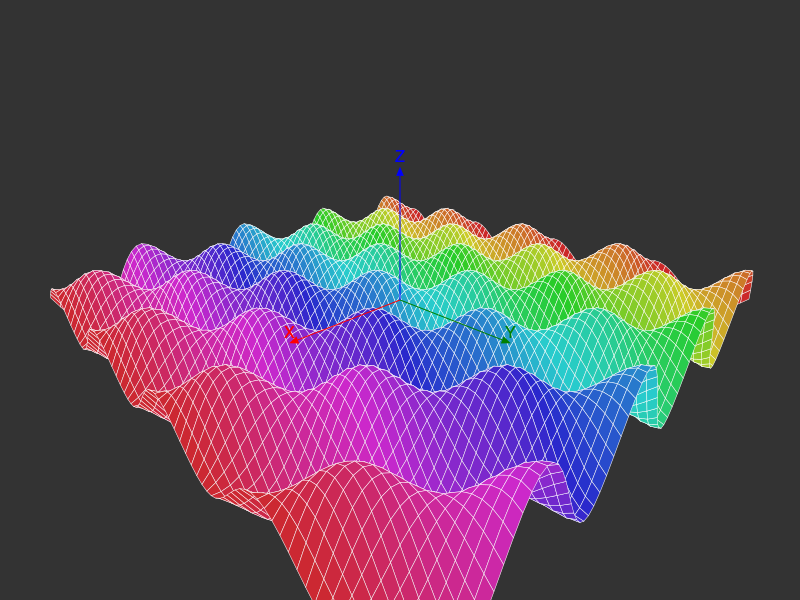
Don't forget to check out Makie.jl for genuine 3D plotting...